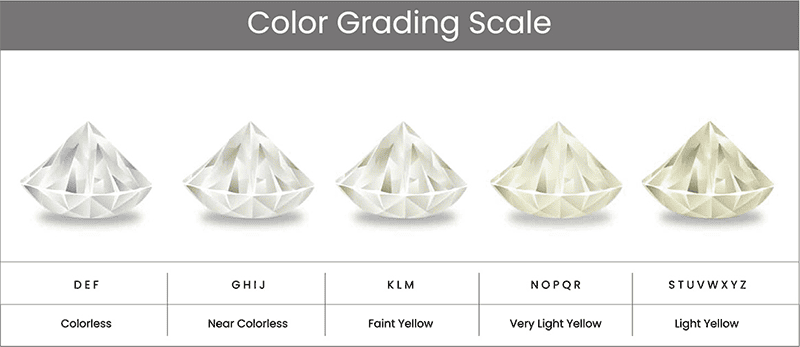
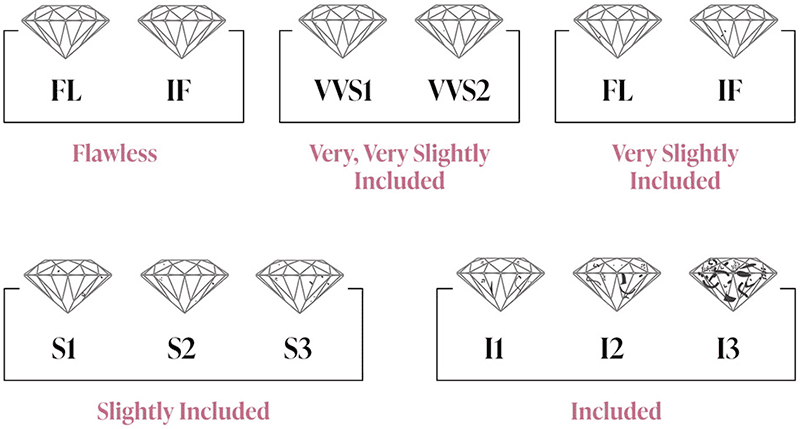
The cut of a diamond pertains to the manner in which it has been shaped and faceted to engage with light. This characteristic significantly influences the diamond’s brilliance, fire, and overall sparkle. A diamond that is expertly cut reflects light in a captivating manner, resulting in a stunning visual effect.
- Proportions: Includes depth, table size, and angles.
- Symmetry: Refers to the accuracy of the diamond’s facets.
- Polish: Indicates the smoothness of the diamond’s surface.
- Diamonds with an Excellent Cut: exhibit extraordinary brilliance with well-proportioned patterns.
- Very Good Cut: diamonds display remarkable sparkle and fine polish, contributing to a balanced and symmetrical look.
- Good Cut" diamonds offer noticeable sparkle, along with sufficient polish and symmetry.
- Fair Cut" diamonds reveal limited brilliance and polish, often characterized by less precise symmetry.
- Poor Cut: diamonds are deficient in brilliance and symmetry, frequently appearing dull with uneven surfaces.